Clone
The git clone command is used to create a copy of a remote repository on your local machine in order to make changes that can be later pushed to that remote repository.
This command should only ever need to be done once after creating a new/forked repository in order to get it on the machine that you will be working on and can be done with the following command:
git clone <git-name>
where git-name is the name of the repository as git sees it which can be obtianed from Github under the clone section of the repository.
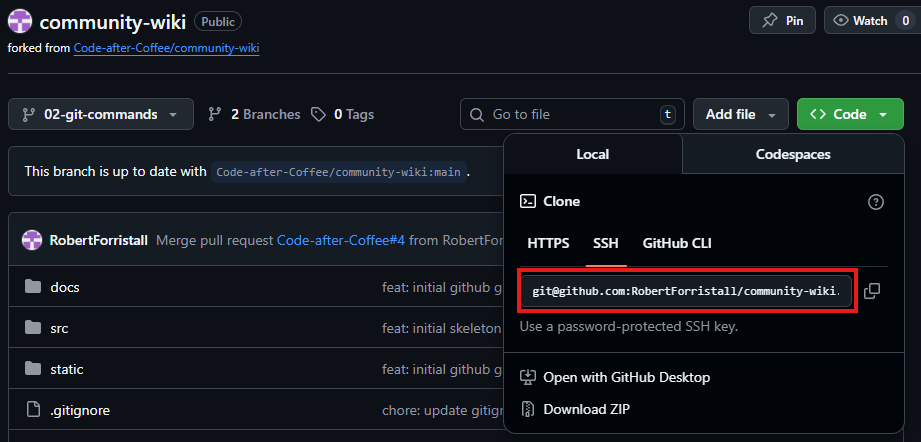
This will pull a copy of the remote repository and place it on your machine in the location that the command was run as a local repository
$ ls
$ git clone git@github.com:RobertForristall/community-wiki.git
Cloning into 'community-wiki'...
Enter passphrase for key '/c/Users/rober/.ssh/id_ed25519':
remote: Enumerating objects: 292, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (292/292), done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (161/161), done.
remote: Total 292 (delta 106), reused 265 (delta 84), pack-reused 0 (from 0)
Receiving objects: 100% (292/292), 1.10 MiB | 3.13 MiB/s, done.
Resolving deltas: 100% (106/106), done.
$ ls
community-wiki/